Advanced RAG¶
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that enhances language models by integrating them with search capabilities. This approach involves the model using data fetched from a search to inform its responses, effectively combining the model's capabilities with external data sources. In 2023, RAG emerged as a leading framework for developing various applications, such as question-answering services that leverage web searches and numerous "chat with your data" apps. This trend also revitalized interest in vector search technologies, leading to the creation of startups focused on vector database solutions, utilizing open-source search indices like faiss, and incorporating additional features for better data handling.
This collection of notebooks implement some of the more advanced RAG techniques.
Basic (Naive) RAG¶
The basic process of RAG involves breaking down texts into smaller pieces, converting these pieces into vectors using a transformer encoder, and storing these vectors in a searchable index. When a query is received, it's also turned into a vector using the same encoding process. The system then searches this vector against the index to find the most relevant text chunks, which are provided to the LLM as context for generating an answer. This method enables the model to produce responses that are informed by a broader context, making the answers more relevant and accurate.
The basic RAG process involves three main steps:
- Chunking - Breaking down texts into smaller pieces
- Vectorization - Converting text chunks into vectors using a transformer encoder
- Vector Store Index - Storing vectors in a searchable index
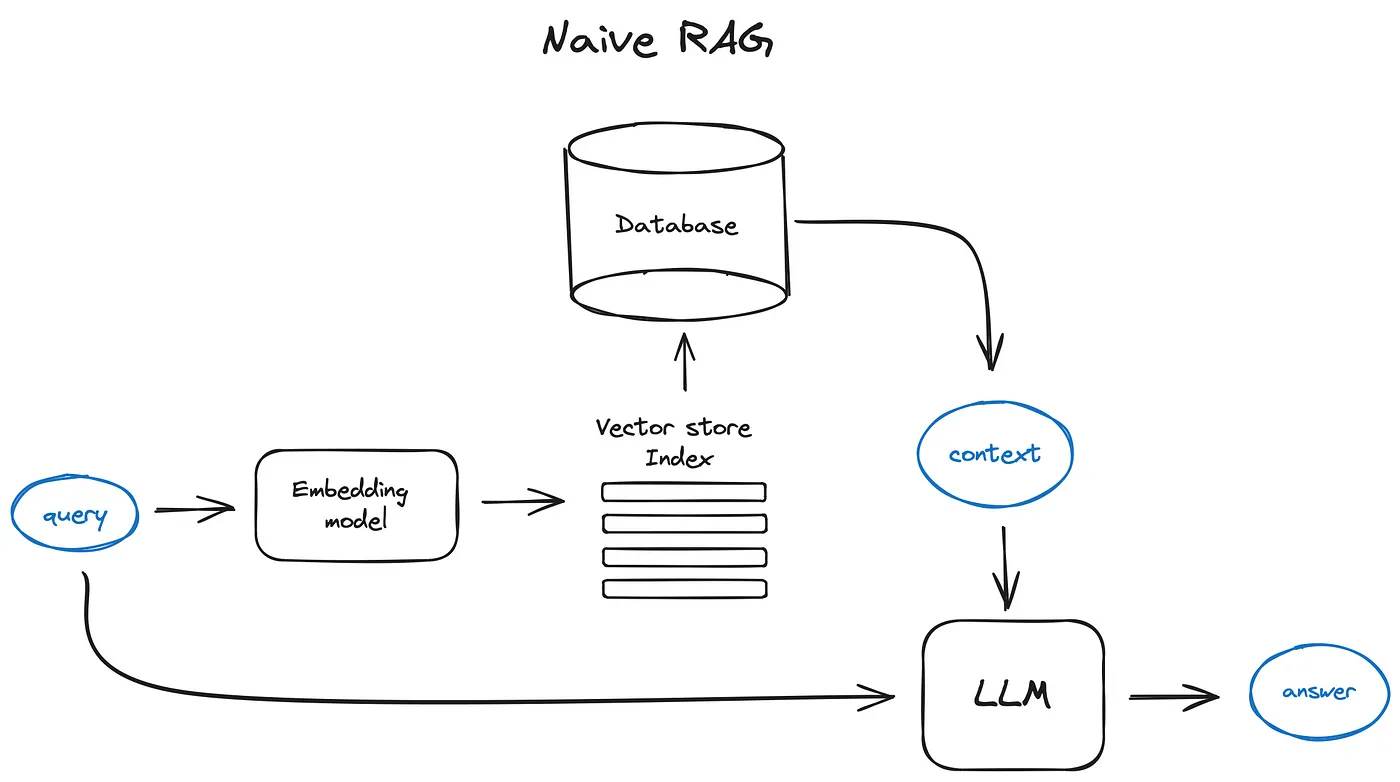
This approach typically yields okay results, but we can do much better. That's why it's sometimes called "naive" RAG.
Advanced RAG¶
Various schemes have have been developed to improve the relevance of retrieved documents and the quality of generated responses. Sometimes called the "RAG Triad", advanced RAG techniques typically try to improve upon:
- Context relevance - Is the retrieved context relevant to the query?
- Groundedness - Is the response supported by the context?
- Answer relevance - Is the response relevant to the query?
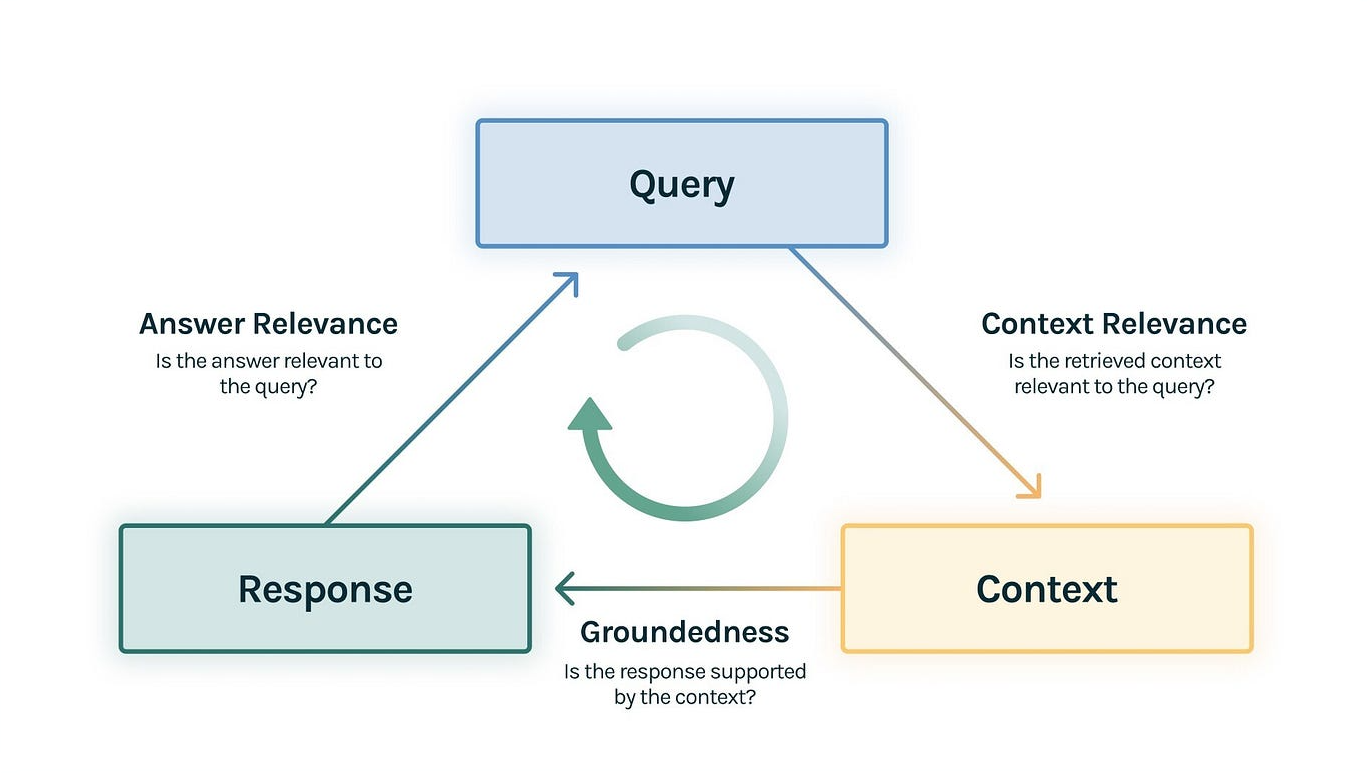 Source: https://www.trulens.org/trulens_eval/getting_started/core_concepts/rag_triad/
Source: https://www.trulens.org/trulens_eval/getting_started/core_concepts/rag_triad/
Advanced RAG techniques can involve more sophisticated retrieval mechanisms, better ways of encoding context, and more effective methods for generating responses. These improvements can significantly enhance the performance of RAG systems, making them more accurate and reliable in a wide range of applications.
Advanced RAG Techniques¶
- Hierarchal Indices - One index for summaries, another for document chunks
- HyDE & Hypothetical Questions - Using an LLM to generate hypothetical answers (or questions) that will have higher semantic similarity to the actual answer (or query).
- Knowledge Graphs - Storing data in knowledge graphs for more structured retrieval
- Context Enrichment: Sentence window retrieval, auto-merging retrieval
- Fusion Retrieval/Hybrid Search - Combining dense and sparse retrieval
- Reranking/Filtering - Reordering the retrieved documents/chunks based on the query before dense embedding search
- Query Transformations: step-back prompting, routing, query rewriting, sub-questions, ReAct agent tool picking
- Chat Engine - using chat history to improve responses
- Query Pipelines & Routing - Chaining worflows or creating query DAGs or translating the query into a set of choices. Useful for multiple data sources like vector, graph, and relational databases
- Tool Use - Incorporating deterministic functions or external APIs like calculators, web searches, etc.
- Response Synthesis - Iteratively sending chunks to LLM, summarizing retrieved context, generating multiple responses
- RAG Fine-tuning (RAFT) - Generating Q&A pairs from two models based on a document, then fine-tuning a model on these pairs
- Tree-Organized Retrieval (RAPTOR) - Recursively clustering and summarizing clusters in layers for retrieval
- All-Sort - Using an LLM to score and sort the retrieved documents/chunks before storing
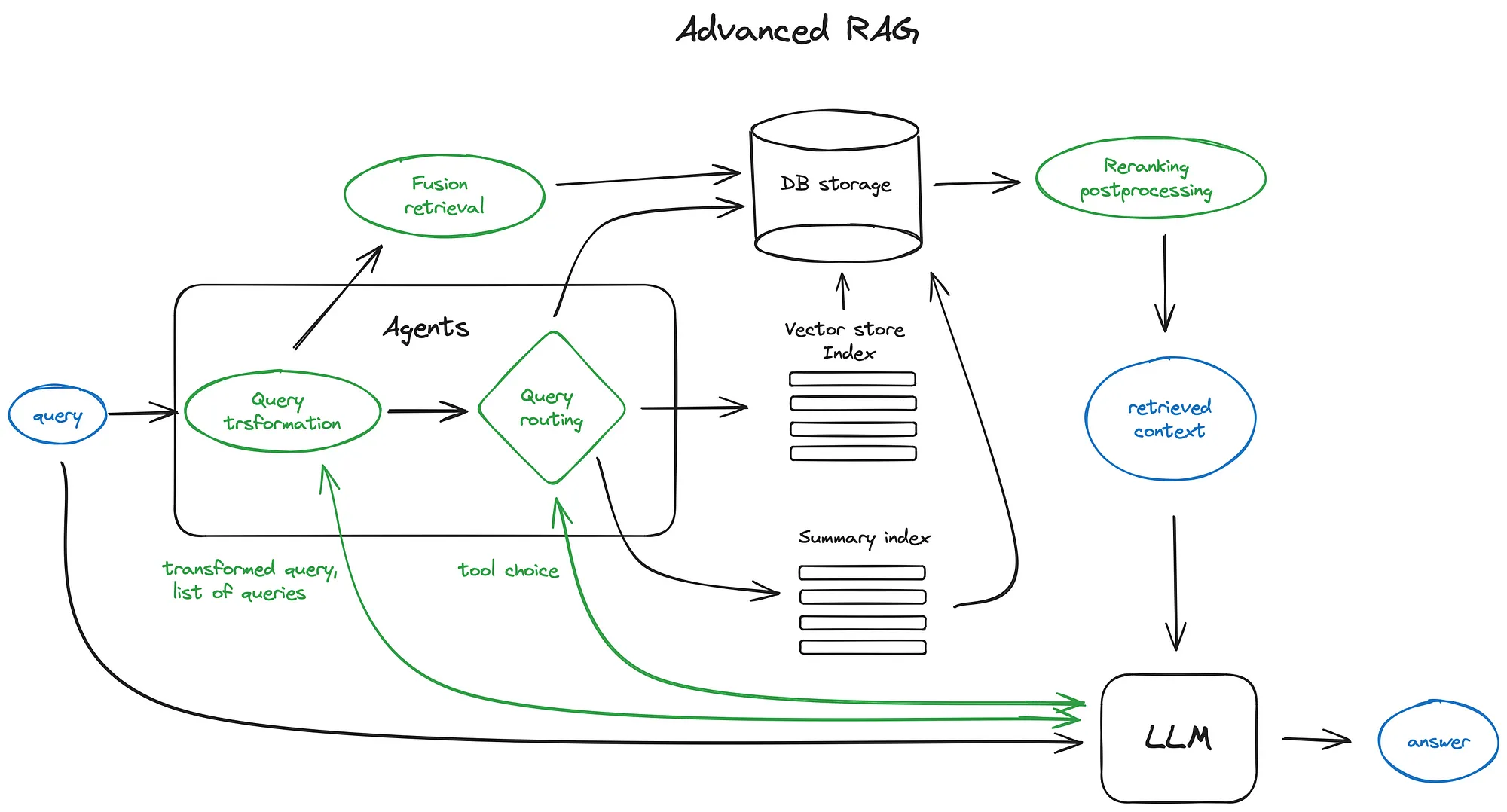 Source: https://pub.towardsai.net/advanced-rag-techniques-an-illustrated-overview-04d193d8fec6
Source: https://pub.towardsai.net/advanced-rag-techniques-an-illustrated-overview-04d193d8fec6